Table 4 of the masonry code (TMS 402/602) sets forth a profusion of masonry special inspections applicable to masonry structures, but not nearly all of them. Table 4 is entitled “Minimum Special Inspection Requirements.” However, code readers should not take the title literally because there are numerous additional special inspections and tests required by the masonry code beyond those cited in the reference columns of Table 4. Some of these masonry special inspections are so subtle (ambiguous) that they are easy to miss entirely.
Portion of TMS 602 – Table 4
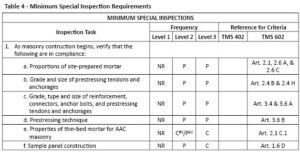
Using the portion of Table 4 shown above, we will select a specific inspection task, such as 1a, which addresses proportions of site-prepared mortar. The “frequency” column indicates that periodic special inspections are required for Level 2 and Level 3 projects. You track to the extreme right-hand reference column identified as TMS 602, which exhibits Articles 2.1, 2.6A, and 2.6C. These articles explain the code acceptance criteria involving the special inspection tasks related to mortar that is site-prepared:
- Mortar must comply with ASTM C 270, “Standard Specification for Masonry ”
- How long to mix the masonry mortar at the project site (3 to 5 minutes).
- Addresses mortar re-tempering and how long mortar can be used after being mixed, which is 2 ½ hours after initial mixing.
There are approximately 14 individual special inspection tasks listed in the inspection task column and corresponding TMS 402 sections and TMS 602 articles listed in the Reference Criteria Column that should be reviewed to apply the appropriate project special inspections.
There are dozens of masonry special inspections required by TMC 602, Table 4, but dozens upon dozens more special inspections are chronicled in TMS 602 that are not explicitly mentioned in Table 4. Within the approximate 66 pages of TMS 602, between Article 1.4 and Article 3.8, many inspections tasks and tests are addressed which represent masonry code-required acceptance criteria that the masonry special inspector should observe during masonry construction. Some of them (but not all) are as follows:

- Some unit strength test and inspection methods, including mock- up panels, must be accomplished before masonry construction commences to comply with Table 3 requirements to verify compliance of masonry system components. Article 1.4B
- Before masonry construction, verify compliance of Table 3
- During construction, verification of proportions of materials as delivered to the project site for premixed or preblended mortar and grout, other than self-consolidating The primary goal is to monitor compliance with ASTM C 270. Table 3
- The code and ASTM C1586 require that the project inspection includes verification of mortar proportioning through observation. The method of measuring material quantities for the mortar used in construction must accurately maintain the code-required proportions (specified by ASTM C 270).
- Masonry protection: Cover the top of unfinished masonry work to protect it from moisture intrusion. Article 1.8B
- Cold weather construction: When ambient air temperature is below 40°F, implement cold weather procedures as required by Article 8C. Dozens of these procedures range from heating the mortar mix water, heating the masonry sand, and heating the masonry units.
- Hot weather construction: Implement approved hot weather procedures and comply with the provisions of Article 1.8D. Numerous hot weather provisions must be adhered to, including the use of windbreaks, minimum and maximum mortar temperatures, maintaining masonry sand plies in a damp and loose condition, and the duration after initial mixing that mortar can be used.
- Provide masonry mortar of the type and color specified, conforming to ASTM C.
- Unless otherwise required, provide grout that conforms to the requirements of ASTM C 476 (Minimum compressive strength of 2,000 psi). Article 2.2
- Provide concrete masonry units that conform to the applicable requirements of ASTM C55, C73, C90, C129, C744, or C1634 as specified. Article 2.3
- Reinforcing bars: Provide deformed reinforcing bars that conform to the approved ASTM designations listed in Article 2.4.
- Before the start of masonry construction, the contractor shall verify that foundations are constructed within a level alignment tolerance of ± ½ inch and that reinforcing dowels are positioned according to the project drawings. Article 3.1
- Clean reinforcement and shanks of anchor bolts by removing mud, oil, and other materials that would adversely affect the bond at the time mortar or grout is placed. Article 3.2
- Place reinforcement and ties in grout spaces before grouting. (No wet sticking of rebar allowed). Construct grout spaces free of mortar droppings, debris, loose aggregates, and any material deleterious to masonry Articles 3.2D and 3.2E
- Unless otherwise required, construct 3/8-inch-thick bed and head joints except for when exceptions are Unless otherwise required, tool the joint with a round jointer when the mortar is thumbprint hard. Remove masonry mortar protrusions extending ½ inch or more into the cavities to be grouted. Article 3.3B
- Place hollow concrete masonry units so that face shells of bed joints and webs are fully Article 3.3B
- Dimensional tolerances are listed for head and bed joints under various project site Variations from level and true to line tolerances are specified. Article 3.3F
- Joint reinforcement: Place joint reinforcement so that longitudinal wires are embedded in mortar with a minimum cover of ½ inch when not exposed to weather or earth, OR 3/8 inch when exposed to weather or Article 3.4B
- Provide a minimum 6-inch lap splice for joint Ensure that the ends of longitudinal wires of joint reinforcement at laps are embedded in mortar or grout. Article 3.4B
- Embed the ends of wall ties in mortar joints. Embed wall tie ends at least ½ inch into the outer face shell of hollow Embed wire wall ties at least 1 ½ inches into the mortar bed of solid masonry units or solid grouted hollow units. Article 3.4C
- Anchor bolts: Embed headed and bent-bar anchor bolts larger than ¼ inch diameter in grout that is placed in accordance with Article 5A and Article 3.5B. Anchor bolts of ¼ inch diameter or less are permitted to be placed in grout or mortar bed joints that have a specified thickness of at least ½ inch. Article 3.4D
- Grout placement: Place grout within 1 ½ hours from introducing water in the mixture and before initial set. Article 3.5
- Grout consolidation: Consolidate grout at the time of Consolidate grout pours 12 inches in height or less by mechanical vibration or puddling. Consolidate pours exceeding 12 inches in height by mechanical vibration, and reconsolidate by mechanical vibration after initial water loss and settlement has occurred. Article 3.5E
- Grout key: When grouting, form grout keys between grout Form grout keys between grout lifts when the first lift is permitted to set before placement of the subsequent lift. Form a grout key by terminating the grout a minimum of 1 ½ inches below the top bed joint. Article 3.5F
The individual bullet points denoting masonry code acceptance criteria do not include all of the dozens of acceptance criteria set forth in the TMS 602 Specifications part of the masonry code. The bullet point items listed do represent some of the major masonry code acceptance items.
__________
Trouble Deciphering the Code? Call the Experts at F&R!
Contact Alan S. Tuck, Director of Code Compliance & Training, Author of Speaking in Code
T 540.344.7939 | M 540.798.4440 | [email protected]
For a complete picture of the Code and how it relates to Special Inspections, F&R would love to provide a virtual AIA-accredited Lunch & Learn presentation to the professionals at your firm.






