SPEAKING IN CODE – STRUCTURAL STEEL SPECIAL INSPECTIONS REQUIRED BY CODE
(According to Chapter N of AISC 360)
Dozens of code books and code reference standards contribute thousands of pages addressing structural steel inspections. This edition of Speaking in Code covers Chapter N of AISC 360 – Specifications for Structural Steel Buildings, which is entitled, “Quality Control and Quality Assurance.” This chapter is a total of 27 pages; 12 pages are devoted to the actual CODE, and 15 pages are devoted to code commentary that attempts to use plain, simple verbiage to explain and clarify what the first 12 pages of the CODE actually mean.
Chapter N provides minimum requirements for quality control (QC), quality assurance (QA), and nondestructive testing (NDT) for structural steel systems and steel elements of composite members for buildings and other structures. Minimum observation and inspection tasks deemed necessary to ensure quality structural steel construction are defined. This chapter also defines comprehensive “Quality Control” requirements on the part of the steel fabricator and erector. Also included are similar requirements for “Quality Assurance” on the part of the project owner’s representatives when such is deemed necessary to complement the contractor’s quality control function. These follow the same requirements for inspections used in AWS D1.1 and the Research Council for Structural Connections (RCSC) Specification for high strength bolts.
Chapter N consists of seven well defined sections and they are as follows:
N1. General Provisions
N2. Fabricator and Erector Quality Control Program
N3. Fabricator and Erector Documents
N4. Inspection and Nondestructive Testing Personnel
N5. Minimum Requirements for Inspection of Structural Steel Buildings N6. Approved Fabricators and Erectors
N7. Nonconforming Material and Workmanship
The terms quality control and quality assurance are used throughout Chapter N to describe inspection tasks required to be performed by the steel fabricator, erector, and project owner’s representatives respectively. The QA tasks are inspections often performed when required by the applicable building code or authority having jurisdiction (AHJ) and designated as “Special Inspections” or as otherwise required by the project owner or Engineer-of-Record.
Chapter N identifies and defines two inspection levels for required inspection tasks and labels them as either observe or perform. The choice in terminology reflects the multi-task nature of welding and high-strength bolting operations as well as the required inspections during each specific phase. The definition of the terms observe and perform vary slightly depending on which code or standard you cite. AISC 360 Chapter N cites the language used by AWS D1.1 (Structural Welding Code) and defines the term observe as “observe these items on a random basis” and the term perform as “perform these tasks on each welded joint or member.” The terms observe and perform replaced the terms periodic and continuous respectively several code cycles ago (IBC 2012) for the structural steel discipline.
Understanding the meaning of observe and perform is important in order to properly understand and utilize the numerous tables included in Chapter N that denote dozens of inspection tasks to be provided by the special inspector. AWS D1.1 describes observe tasks and also defines the frequency of these tasks to be “at suitable intervals.” Perform tasks are required for each weld by AWS D1.1 and are necessary for final acceptance of the weld or item. The use of the term perform is based upon the use in AWS D1.1 phrases “shall examine the work” and “size and contour of welds shall be measured”; hence, perform items are limited to those functions typically performed at the completion of each weld. The words all welds in AWS D1.1 clause 6.5.1 clearly indicate that ALL welds are required to be inspected for size, length, and location in order to ensure conformity. Chapter N follows the same principle in labeling these tasks perform, which is defined as “perform these tasks for each welded joint or member.”
The words suitable intervals used in AWS D1.1 characterize that it is not necessary to inspect these tasks for each weld but as necessary to ensure that the applicable requirements of AWS D1.1 are met. Following these same principles and terminology, Chapter N labels these tasks as observe, which is defined as “observe these items on a random basis.” The term suitable intervals is not defined within Chapter N or AWS D1.1 other than the AWS statement, “to insure that the applicable requirements of this code are met.” The suitable intervals that apply to specific projects must, ultimately, be decided by the project special inspector because the establishment of suitable intervals is dependent upon the QC program of the fabricator and erector, the skills and knowledge of the welders themselves, the type of weld, and the importance of the weld, etc. Increased levels of observation are often required during initial stages of construction versus later stages of construction for a host of reasons.
AISC 360 and Chapter N includes six tables which list most of the code-required special inspections in an easy to understand tabular format. Tables N5.4-1, N5.4-2, and N5.4-3 list the inspection tasks prior to welding, during welding, and after welding. Chapter N Tables N5.6-1, Table N5.6-2, and N5.6-3 list the inspection tasks prior to bolting, during bolting, and after bolting. These tables address dozens of special inspections and tests that must be provided by the special inspector during construction phases of the project. Prior to the creation of these tables in Chapter N, the special inspector, registered design professional, contractor, and building official would all have to research hundreds or thousands of pages in numerous building codes in order to apply the code-required tasks and tests. These are addressed in the Chapter N tables in just twelve pages of code narrative.
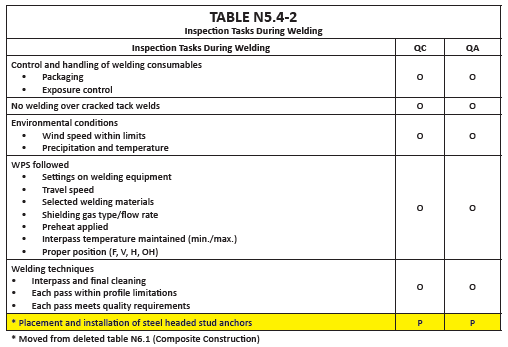
It should be noted that in the most recent edition of AISC 360 (2016), Table N6.1, which addressed the “Inspection of Steel Elements of Composite Construction,” has been DELETED. The old Table N6.1 line item and verbiage that addressed “placement and installation of steel headed stud anchors” can now be found in Chapter N, Table N5.4-2, “Inspection Tasks during Welding.” Also, Chapter A, section A2 of AISC 360-16 invokes the Steel Deck Institute’s (SDI) QA/QC manual (2011 edition) entitled, “Quality Control and Quality Assurance for Installation of Steel Deck.”
AISC 360, Chapter N, section N5 – Nondestructive Testing of Welded Joints has several significant changes in the 2016 edition of the code and they are as follows:
5a. Procedures
This section has been edited for clarity. The User Note has been replaced with a new one directing users to Section M2.4 for additional information.
5b. CJP Groove Weld NDT
This section has been edited for clarity.
5c. Welded Joints Subjected to Fatigue (moved from Section N5.5d)
The provisions were replaced with the 2010 Section N5.5d provisions.
5d. Ultrasonic Testing Rejection Rate (new Section)
This new section is used to determine the rejection rate of ultrasonic testing. Some content is moved here from the 2010 Section N5.5e, Reduction of Ultrasonic Testing Rate.
5e. Reduction of Ultrasonic Testing Rate
Renamed – formerly called “Reduction of Rate of Ultrasonic Testing.” A statement has been added specifying that for projects that contain 40 or fewer welds there should be no reduction in the ultrasonic testing rate. All content on length of welds for evaluating the reject rate has been moved to Section N5.5d. This section has also been edited for clarity.
5f. Increase in Ultrasonic Testing Rate
Renamed – formerly called “Increase in Rate of Ultrasonic Testing.” All content on lengths of welds for evaluating the reject rate has been moved to Section N5.5d. This section has also been edited for clarity.
N5.6 Inspection for High Strength Bolting
This section has been edited for clarity.
Table N5.6-1 Inspection Tasks Prior to Bolting
This table has been edited for clarity.
Table N5.6-2 Inspection Tasks During Bolting
This table has been edited for clarity.
N5.7 Inspection of Galvanized Structural Steel Main Members (New Section)
This new section identifies the need for inspection of galvanized structural steel main members.
N5.8 Other Inspection Tasks (Moved from N5.7)
This section has been rearranged and some content divided into User Notes. This section has also been edited for clarity.
N6. Approved Fabricators and Erectors (Moved from N7)
This Section has been edited for clarity. The material in this Section was removed because it is now covered by the Steel Deck Institute (SDI).
N7. Nonconforming Material and Workmanship (Moved from N8)
No changes have been made to this section.
While this particular Speaking in Code article is focused on the significant changes in AISC 360-16 Chapter N versus the old AISC 360-10 Chapter N, there are other important changes in the newer AISC 360-16, “Specification for Structural Steel Buildings.” AISC 360 Chapter A has added ASTM F3125, “Standard Specification for High Strength Bolts.” F3125 includes the former A325 and A490 type standards as grades; thus, ASTM A325, A490, F1852, and F2280 no longer exist as separate standards.
ASTM F3111, “Standard Specification for Heavy Hex Structural Bolt/Nut/Washer Assemblies,” and ASTM F3043, 200, “Hex Head and Twist-Off Bolts,” are added as a new AISC Group C. Because of their very high strength, the use of Group C assemblies is limited to specific building locations and noncorrosive environmental conditions by the ASTM standards.
But Wait — We Have a Lot More to Say!
For a complete picture of the Code and how it relates to Special Inspections, F&R would love to provide a virtual (for the time being) AIA accredited Lunch & Learn presentation to the professionals at your firm.
Alan S. Tuck
Director of Code Compliance & Training
T 540.344.7939
M 540.798.4440
atuck@fandr.com

